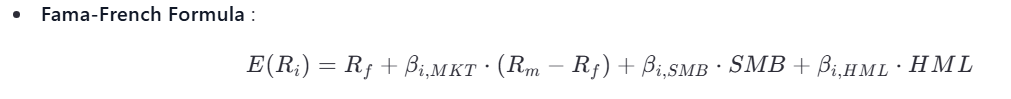Lecture 9: Other Models for Analyzing the Relationship Between Return and Risk
1. Arbitrage Pricing Theory (APT): Concept and Differences from CAPM
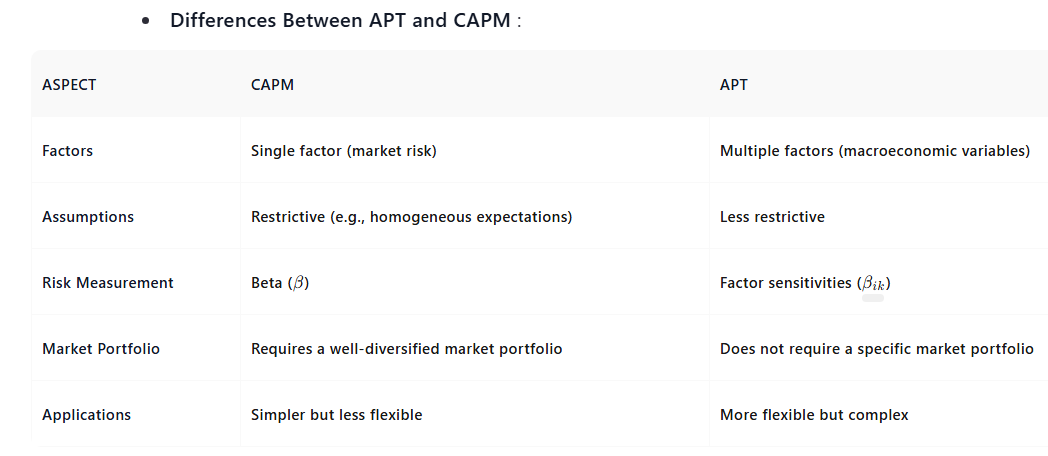
The Arbitrage Pricing Theory (APT) , developed by Stephen Ross in 1976, is an alternative to the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) for explaining the relationship between risk and return. Unlike CAPM, which is a single-factor model, APT is a multi-factor model that incorporates multiple sources of systematic risk.
-
Key Concepts of APT :
- APT assumes that asset returns are influenced by multiple macroeconomic factors, rather than just market risk () as in CAPM.
- The model does not require restrictive assumptions like homogeneous expectations or a single-period framework.
- APT relies on the principle of arbitrage , where investors exploit mispriced assets to earn risk-free profits, driving prices back to equilibrium.
-
APT Formula :
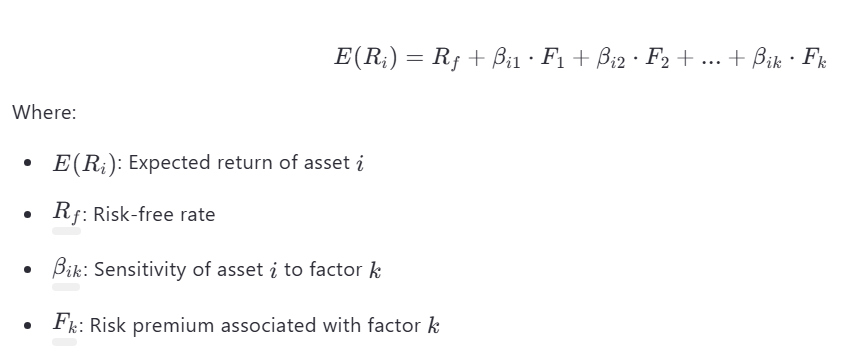
2. Fama-French Three-Factor Model: Additional Factors
The Fama-French Three-Factor Model , introduced by Eugene Fama and Kenneth French in 1993, extends the CAPM by incorporating additional factors that explain variations in stock returns beyond market risk.
-
Additional Factors :
- Market Risk (MKT) :
Similar to CAPM, this factor measures the sensitivity of an asset’s returns to market movements.
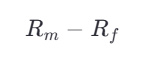
-
Size Factor (SMB - Small Minus Big) :
Captures the tendency of small-cap stocks to outperform large-cap stocks. -
Value Factor (HML - High Minus Low) :
Reflects the tendency of value stocks (high book-to-market ratio) to outperform growth stocks (low book-to-market ratio).-
Advantages of the Fama-French Model :
- Provides a better explanation of stock returns compared to CAPM.
- Accounts for anomalies like the size effect and value effect, which CAPM cannot explain.
3. Comparison Between Different Models
-